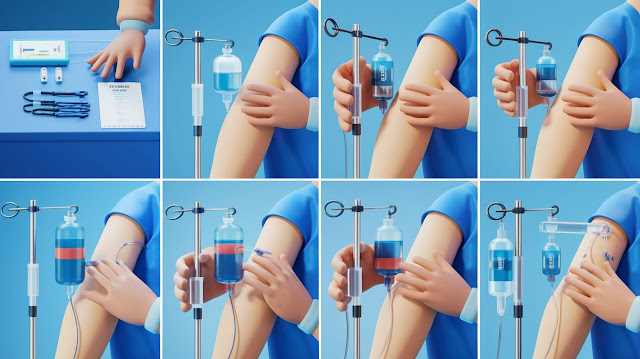
1. Gather Equipment Before you begin, ensure you have all necessary equipment ready:IV cannula (size appropriate for the patient, typically 18-24 gauge)TourniquetAlcohol swab or antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine or iodine).Sterile glovesAdhesive dressing or IV securing deviceSaline flush (optional, to check for patency)TapeSharps disposal containerIV extension set or tubing (if connecting to an infusion)2. Explain the Procedure to the PatientReassure the patient, explaining the need for the IV and the steps involved.Position the patient comfortably and ensure good lighting at the site.3. Select the Insertion Site Choose a vein: Preferred sites include the dorsal veins of the hand or the cephalic, basilic, or median cubital veins in the...


 September 29, 2024
September 29, 2024